Bonding magnets plays a central role in the reliability and functionality of magnetic assemblies. In a wide range of applications, such as electric motors, actuators, sensors, and loudspeakers, magnets are exposed to high temperatures, mechanical forces, and vibrations. The quality of the adhesive joint has a direct impact on the performance and lifespan of the final product.
Within the production processes at Bakker Magnetics, bonding magnets is an integral part of the overall assembly. The combination of material expertise, precise tolerances, and controlled process steps leads to stable and reproducible results.

The role of the bonding process in magnetic assemblies
An adhesive joint in a magnetic application must function under varying conditions. During use, magnets are subjected to:
- high thermal loads
- prolonged vibrations
- mechanical shocks
- centrifugal forces during rotation
- environmental influences such as moisture and chemicals
A carefully applied adhesive joint prevents shifting, damage, or detachment of magnets, thereby supporting the reliability of the complete assembly.

The importance of the correct bond line
The bond line, the distance between the magnet and the substrate, determines the final strength and durability of the joint. Within production processes, controlled, application-specific bond lines are used, including:
- Epoxy: 0.05 – 0.15 mm
- Structural acrylics: 0.1 – 0.25 mm
- Cyanoacrylate: < 0.05 mm
A consistent bond line contributes to even stress distribution and predictable curing.
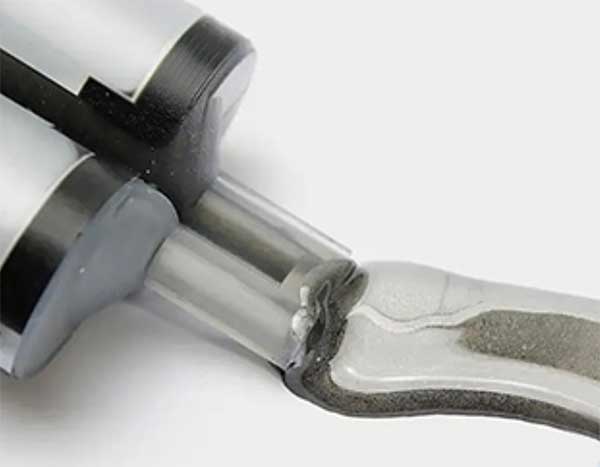

1- and 2-component adhesive systems
Various adhesive technologies are used in magnetic assemblies, depending on process requirements.
1-component systems
These adhesives consist of a single formula and cure through heat, humidity, or an activator. They are often chosen when high production speed and process consistency are key.
2-component systems
Here, resin and hardener are combined. This type of adhesive is less sensitive to environmental conditions and is used when structural strength and temperature stability are required.
The choice between these systems depends on the production process, required mechanical properties, and material characteristics.
Temperature performance of adhesives
Magnetic assemblies are often exposed to large temperature variations. The thermal resistance of the adhesive system largely determines its suitability for a specific application. Examples of temperature stability include:
- Cyanoacrylate: approx. 90–120 °C
- Structural acrylics: up to approx. 200 °C
- Epoxy systems: around 150 °C
- High-temperature epoxies: up to approx. 250 °C with additional heat curing
These temperature limits are matched to the environment in which the assembly operates.
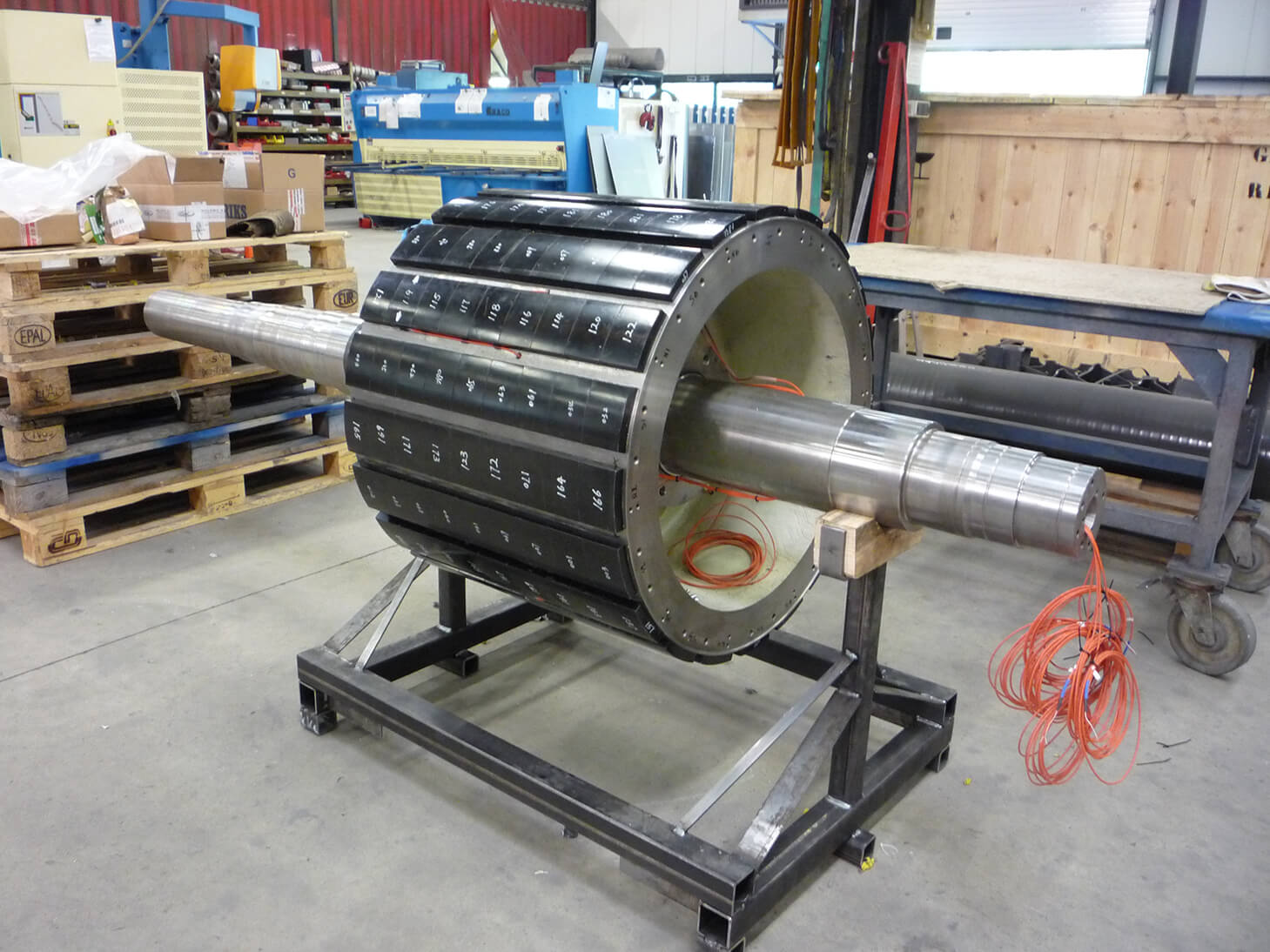

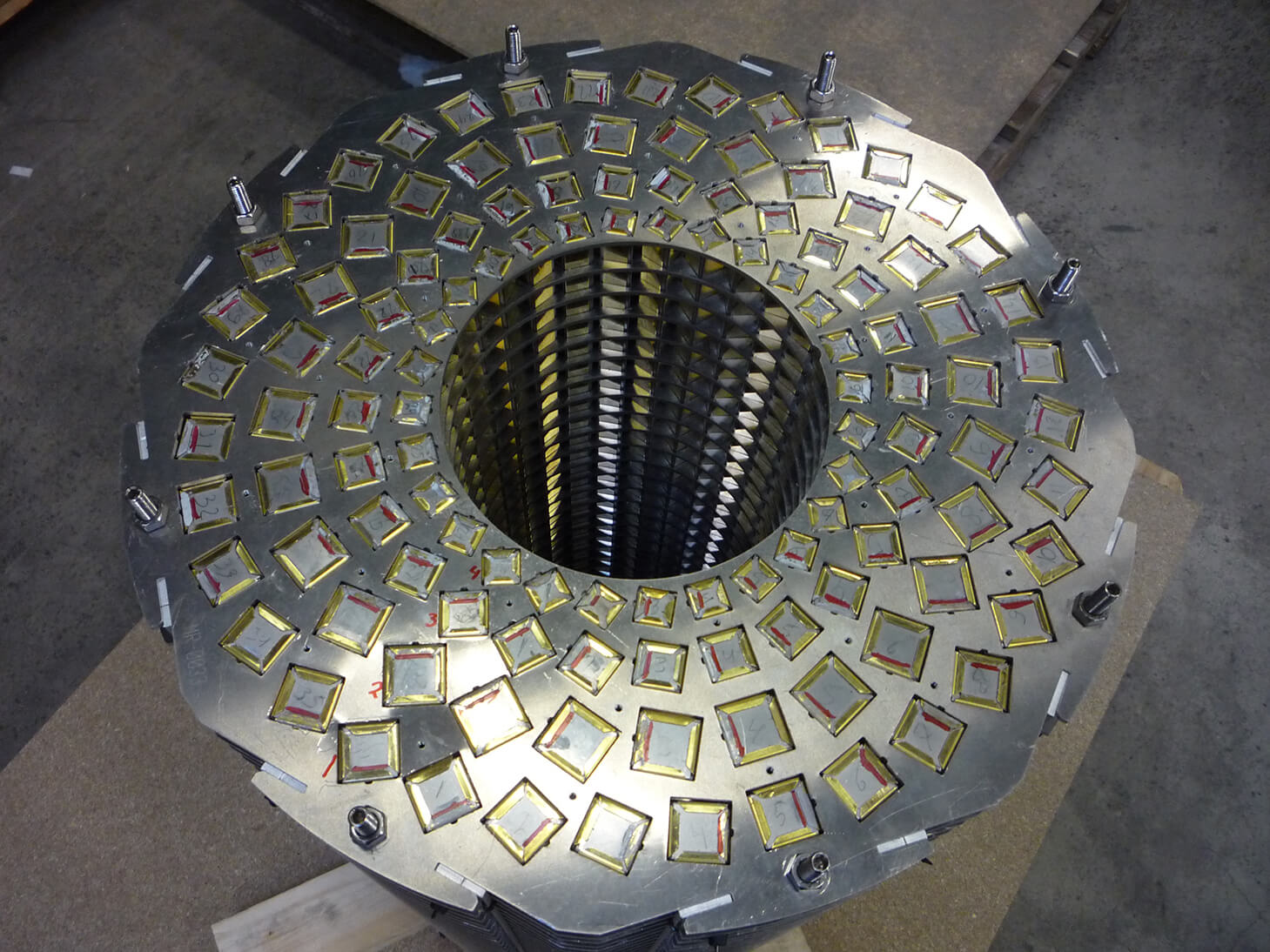
Rotational systems and mechanical loading
In high-speed applications, centrifugal forces play an important role. The quality of the bonding process influences resistance to:
- dynamic loads
- continuous vibrations
- structural deformation
In high-speed motors, adhesive joints are therefore created to withstand long-term and repetitive mechanical loading. Depending on design requirements, additional techniques may be used, such as bandages, groove connections, or mechanical housings.
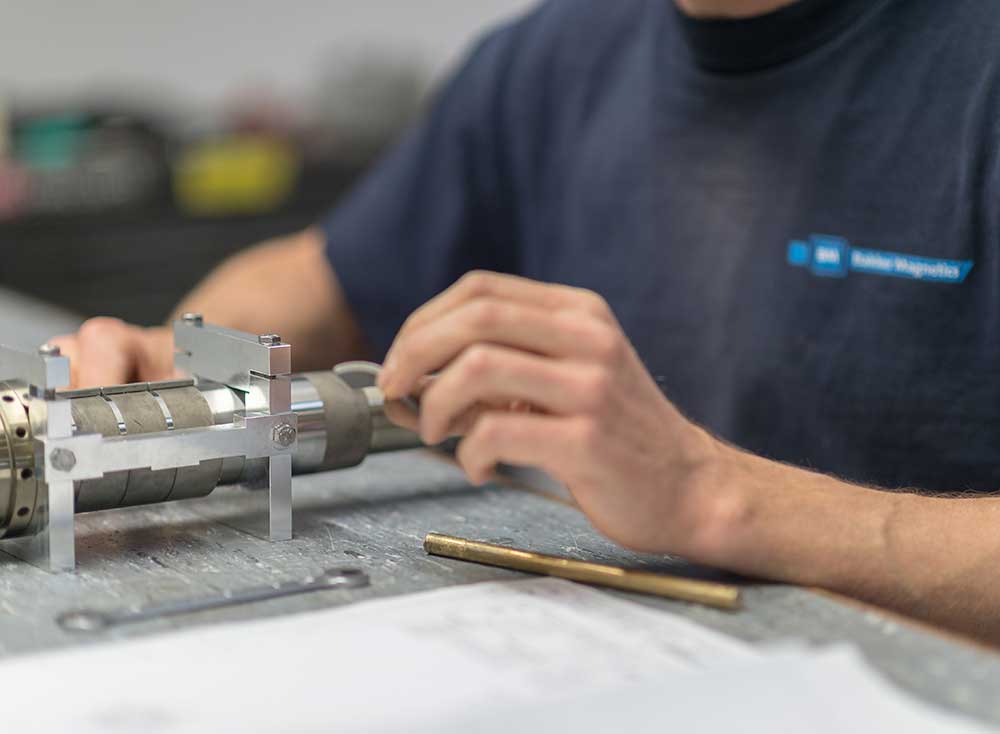

Processing different magnet materials
Magnet materials such as NdFeB, SmCo, AlNiCo, and ferrite each have different properties regarding hardness, brittleness, corrosion resistance, and temperature behavior. The bonding process takes into account:
- surface structure
- sensitivity to chipping
- thermal expansion
- desired durability of the joint
These factors determine how magnet and substrate are joined within the required tolerances.
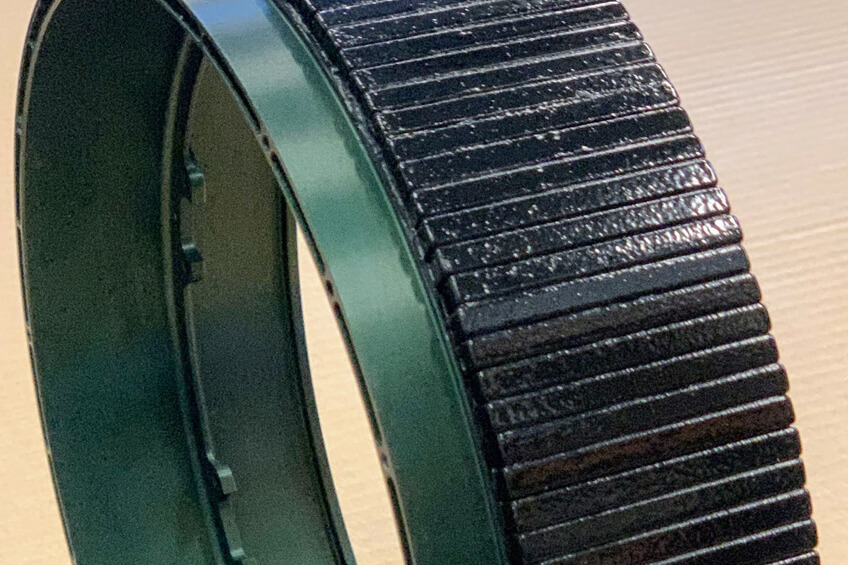
Additional techniques in magnetic assembly
Bonding is often just one step within a broader assembly process. Additional techniques include:
Corrosion protection
Coatings, sealings, or surface treatments that protect against moisture and chemicals.
Mechanical locking
Structural solutions that provide extra stability in load-intensive applications.
Rework and repair
Methods for inspection, correction, and reproduction within existing production flows.
Injection-molded magnets
Combinations of magnetic material and polymers enabling complex shapes and integrated functionality.
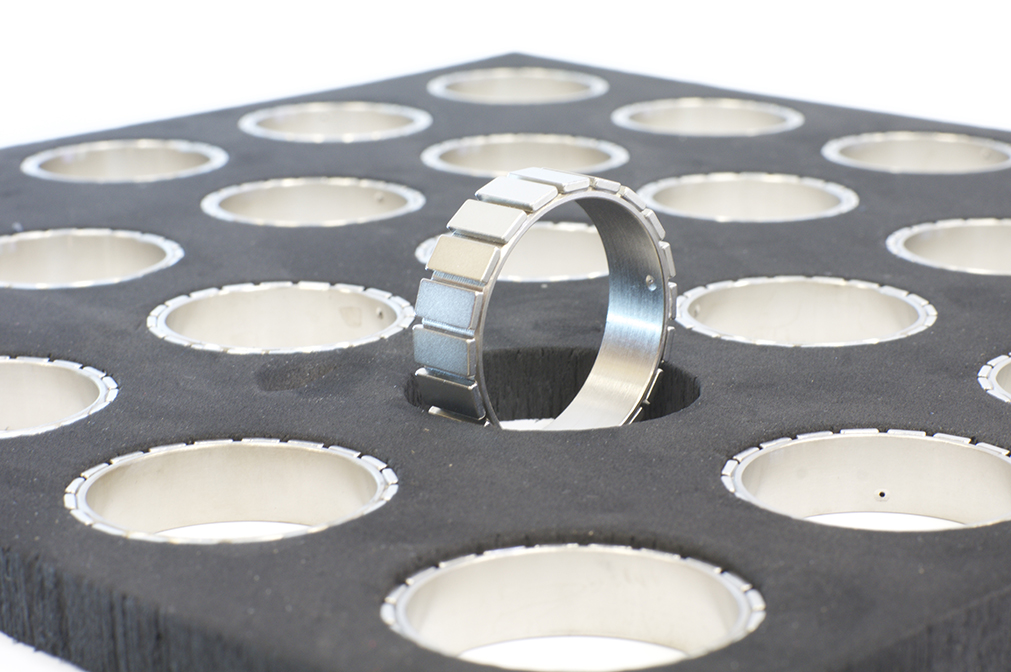

The bonding process determines the quality of your magnetic assembly
Bonding magnets is a technically specialized process that directly affects performance, safety, and lifespan. By using the right materials, adhesive systems, tolerances, and process control, Bakker Magnetics creates durable and robust magnetic assemblies that meet the highest industry standards.

Would you like to learn more about magnet bonding or need support for your project? Our engineers are happy to help you optimize the right bonding system for your assembly.







